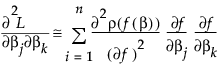Suppose that f(β) is the model. Then the Nonlinear platform attempts to minimize the sum of the loss functions defined as follows:
The second term is probably small if ρ is the squared residual because the sum of residuals is small. The term is zero if there is an intercept term. For least squares, this is the term that distinguishes Gauss-Newton from Newton-Raphson.
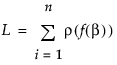
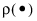 for each row can be a function of other variables in the data table. It must have nonzero first- and second-order derivatives. The default
for each row can be a function of other variables in the data table. It must have nonzero first- and second-order derivatives. The default 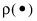 function, squared-residuals, is
function, squared-residuals, is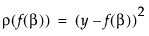
 with respect to the model, and forming the gradient and an approximate Hessian as follows:
with respect to the model, and forming the gradient and an approximate Hessian as follows: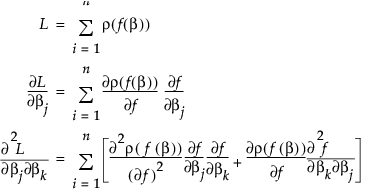
 is linear in the parameters, the second term in the last equation is zero. If not, you can still hope that its sum is small relative to the first term, and use
is linear in the parameters, the second term in the last equation is zero. If not, you can still hope that its sum is small relative to the first term, and use