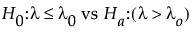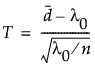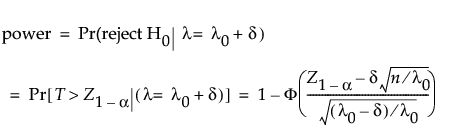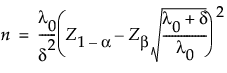where n is the sample size and d is the mean number of defects per unit in the sample. We assume T to be approximately normally distributed. The power calculation is based on the distribution of T under the null and alternative hypotheses.
where Φ() is the standard normal cumulative distribution function and Z1-p is the (1 - p)th quantile of the standard normal distribution.
Using 1 - β to denote the desired power to reject the null hypothesis, the sample size is calculated as follows:
Because an analytical solution for δ does not exist, numerical methods are used to solve for δ given power and n.