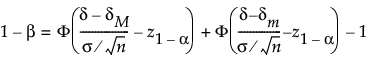Power for One Sample Equivalence
Use the Power Explorer for One Sample Equivalence to determine a sample size for an equivalence test about one mean. Select DOE > Sample Size Explorers > Power > Power for One Sample Equivalence. Explore the trade offs between variability assumptions, sample size, power, significance, and the equivalence range. Sample size and power are associated with the following hypothesis test:
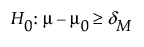 or
or 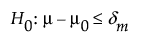
versus the alternative:
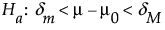
where μ is the true mean, μ0 is the reference value, and (δm, δM) is the equivalence range. For the same significance level and power, a larger sample size is needed to detect a small difference than to detect a large difference. It is assumed that the population of interest is normally distributed with mean μ and standard deviation σ.
Power Explorer for One Sample Equivalence Options
Set study assumptions and explore sample sizes using the radio buttons, text boxes, and sliders. The curve updates as you make changes to the settings. Alternatively, change settings by dragging the cross hairs on the curve or adjusting the values in the axis text boxes.
Equivalence Range
Maximum difference
Specifies the maximum value, above which the mean is considered different from the reference mean
Minimum difference
Specifies the minimum value, below which the mean is considered different from the reference mean.
Note: Typically, the equivalence range is symmetric.
Fixed Parameters
Alpha
The probability of a type I error, which is the probability of rejecting the null hypothesis when it is true. It is commonly referred to as the significance level of the test. The default alpha level is 0.05.
Std Dev (σ)
The assumed standard deviation.
Population standard deviation known
Specifies calculations based on a known population standard deviation.
Test Parameters
Parameters that are inter-related and update as you make changes.
Difference in Means
Specifies the difference between the true mean and the hypothesized or reference mean such that the two means are considered equivalent.
Sample Size
Specifies the total number of observations (runs, experimental units, or samples) needed your experiment.
Power
Specifies the probability of rejecting the null hypothesis when it is false. With all other parameters fixed, power increases as sample size increases.
Save Settings
Saves the current settings to the Saved Settings table. This enables you to save a set of alternative study plans. See Saved Settings in the Sample Size Explorers.
Make Data Collection Table
Creates a new data table that you can use for data collection.
Statistical Details for the One Sample Equivalence Explorer
The power calculations for testing equivalence in one sample group is based on methods described in Chow et al. (2008).
If σ is unknown, the power (1-β) is computed as:
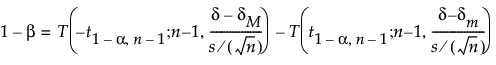
where:
α is the significance level
n is the sample size
s is the standard deviation
δ is the difference to detect
(δm, δM) is the equivalence range
t1-α,ν,is the (1 - α)th quantile of the central t-distribution with ν degrees of freedom
T(t; ν, λ) is the cumulative distribution function of the non-central t distribution with ν degrees of freedom and non-centrality parameter λ.
If σ is known, then power (1-β) is computed as: