Launch the Marker Admixture Platform
To estimate the proportional contribution each population made to each of your samples, launch the Marker Admixture platform by selecting Analyze > Life Sciences > Marker Admixture.
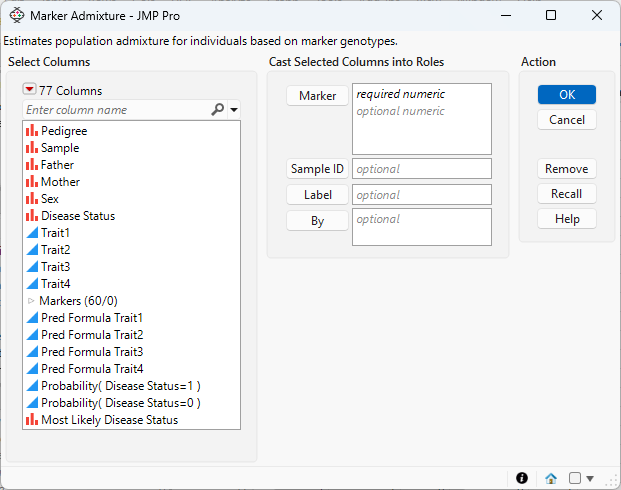
Figure 6.2 The Marker Admixture Launch Window
Marker
Select the marker columns that you want and click Marker to specify the markers that you want to analyze.
Sample ID
Use this option to specify one variable whose value can provide a unique identifier for each row.
Label
Use this option to use the values in the specified column to label the samples in the plots. Values in the specified column do not have to be unique.
By
Produces a separate report for each level of the By variable. If more than one By variable is assigned, a separate report is produced for each possible combination of the levels of the By variables.
Once these options have been specified, click OK to bring up the Marker Admixture - Launch window, where you will specify the remaining options.
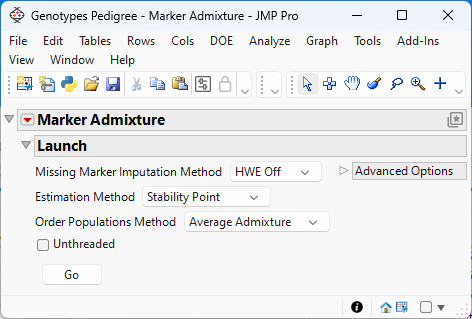
Figure 6.3 The Marker Admixture - Launch window
Missing Marker Imputation Method
Use this option to specify how missing marker values are to be imputed. Because the Marker Simulation method does not run when your data is missing marker data, you must impute any missing data.
– Select HWE Off to impute the missing genotypes with random draws from a multinomial distribution in which the frequency of each genotype class is set to be the observed frequency from the data.
– Select HWE On to impute the missing genotypes with random draws from a multinomial distribution in which the frequency of each genotype class is set to be the expected frequency under the assumption of the Hardy-Weinberg equilibrium (HWE).
– Select Random to randomly assign one of the acceptable values (0, 1, 2, ..., K (where K is the ploidy level)).
– Select Specified to impute the missing genotypes with a specified integer between zero and the ploidy number.
Estimation Method
Use this option to specify the method used to estimate the number of ancestral populations and, hence the number of clusters, to group the samples.
– Select Stability Point to enable the algorithm to calculate the optimum number of ancestral populations.
– Select Fixed Parameter if you know the number of ancestral populations. Specify this number using the Number of Ancestral Populations advanced option.
Order Populations Method
Use this option to specify how individuals are sorted in the report.
– Select Average Admixture to sort the individuals using the average admixture probabilities of the individuals.
– Select Variance Explained to sort the individuals using the variance in the admixture probabilities of the individuals.
Unthreaded
Use this option to suppress multi-threading. Deselect this option for improved computational speed.
Set Random Seed
Use this option to specify a nonnegative integer to start the random number stream. Different values produce different outcomes of the algorithm. This option is available when HWE Off, HWE On, or Random is selected as the imputation method.
Number of Ancestral Populations
Use this option to specify the number of ancestral populations. This option is available only when Fixed Parameter is specified as the Estimation Method.
Imputation Value
Use this option to specify a value to insert into any cell containing a missing value symbol. This option is available only when Specified is selected as the imputation method.
Once these options have been specified, click Go to run the analysis.
Data Format
Most of the processes in JMP assume that the input table has a particular data structure. JMP distinguishes between tall and wide data sets. A tall data table has samples as columns and molecular entity (for example, marker, gene, clone, protein, or metabolite) as rows, whereas a wide data table is the transpose of the tall data table, having the samples as rows and molecular entity as columns.
When specifying the input data set for a process, it is important to know the required form. Marker Imputation requires a wide data table. The Transpose platform under the Tables menu enables you to transform your data tables between tall and wide forms.
Marker data must be encoded in the one-column, numeric format. Typically, in this format, diploid individuals homozygous for the least common, or minor allele, are represented in the table by a 2, whereas the heterozygotes are represented by a 1. Homozygotes for the most common allele are represented by a 0.