Nonparametric Tolerance Intervals
Use the Nonparametric Tolerance Intervals Explorer to determine a sample size for tolerance intervals. A tolerance interval contains a portion p of the population with 100(1 - α) confidence. Select DOE > Sample Size Explorers > Reliability > Nonparametric Tolerance Intervals. Explore the trade-offs between sample size, coverage proportion, the number of observations in the distribution tails, and the confidence level.
Nonparametric Tolerance Intervals Explorer
Set study assumptions and explore sample sizes by using the radio buttons, text boxes, and menus. The profiler updates as you make changes to the settings. Alternatively, you can change the settings by dragging the cross hairs on the profiler curves.
Interval Type
Specifies the type of interval. Specify Lower Bound or Upper Bound for a one-sided interval. Specify Interval for a two-sided interval.
Nonparametric Tolerance Intervals Explorer Profiler
The profiler enables you to visualize the impact of sample size assumptions on the confidence level of your nonparametric tolerance interval. Interactive profiler changes to the sample size or proportion update the calculated interval margin. Interactive changes to the profiler interval margin update the sample sizes. To solve for a specific variable, use the target variable setting and click Go.
Note: Nonparametric tolerance intervals are defined by order or rank statistics. The order statistics are the ordered observations of a data set.
Target Variable
Enables you to solve for the sample size, lowest rank above minimum, or highest rank below maximum.
Confidence Level
Specifies the confidence level of the interval. With all other parameters fixed, the confidence level increases as sample size increases.
Sample Size
Specifies the total number of observations (runs, experimental units, or samples) that are needed to construct your interval.
Lowest Rank Above Minimum
Specifies the order statistic, relative to the 1st order statistic, for the lower bound of the tolerance interval. A Lowest Rank Above Minimum of zero denotes the smallest observation, or the 1st order statistic.
Highest Rank Below Maximum
Specifies the order statistic, relative to the nth order statistic, for the upper bound of the tolerance interval. A Highest Rank Below Maximum of zero denotes the largest observation, or the nth order statistic.
Nonparametric Tolerance Intervals Explorer Options
The Explorer red triangle menu and report buttons provide additional options:
Simulate Data
Opens a data table of simulated data that are based on the explorer settings. View the simulated response column formula for the settings that are used. Run the table script to analyze the simulated data.
Make Data Collection Table
Creates a new data table that you can use for data collection. The table includes scripts to facilitate data analysis.
Remember Settings
Saves the current settings to the Remembered Settings table. This enables you to save a set of alternative study plans. See Remembered Settings in the Sample Size Explorers.
Reset to Defaults
Resets all parameters and graphs to their default settings.
The Profiler red triangle menu contains the following option:
Optimization and Desirability
Enables you to optimize settings. See “Desirability Profiling and Optimization” in Profilers.
Note: The sample size explorer report can be saved as a *.jmpdoe file. Open the file to return to the explorer. An alert prompts you to save the file.
Example of the Nonparametric Tolerance Intervals Explorer
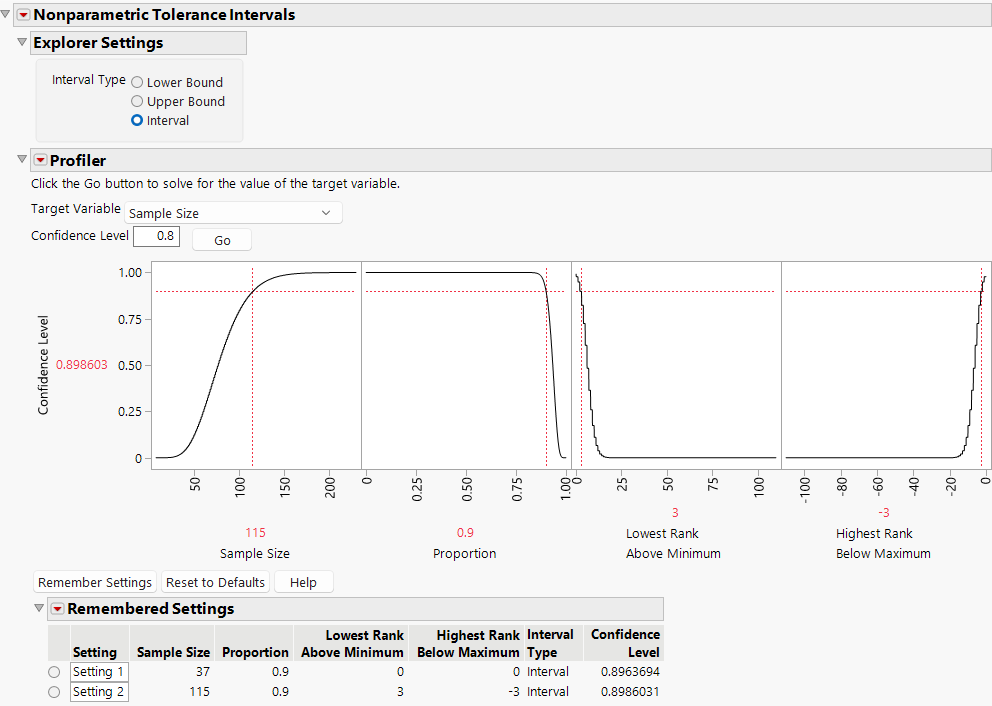
In this example, use the Nonparametric Tolerance Intervals Explorer to explore the sample size and order statistics to define tolerance intervals to cover 90% of your population with 90% confidence.
1. Select DOE > Sample Size Explorers > Reliability > Nonparametric Tolerance Intervals.
2. Leave Interval Type set to Interval for estimating a sample size for a two-sided tolerance interval.
3. Leave Target Variable set to Sample Size.
4. Set Confidence Level to 0.90.
5. Click Go.
6. Click Remember Settings.
7. In the window, leave the default setting name and click OK.
8. In the profiler, set the Lowest Rank Above Minimum to 3.
9. In the profiler, set the Highest Rank Below Maximum to -3.
10. Click Go.
11. Click Remember Settings.
12. In the window, leave the default setting name and click OK.
Figure 29.13 Nonparametric Tolerance Intervals Explorer
The first remembered setting saved the sample size estimation of 37 samples. The minimum and maximum observations from a sample size of 37 defines a tolerance interval that covers 90% of your population with 89.63% confidence. The second remembered setting saved the sample size estimation of 115 samples. The 3rd and 112th order statistics from a sample size of 115 defines a tolerance interval that covers 90% of your population with 89.86% confidence.
Statistical Details for the Nonparametric Tolerance Intervals Explorer
The confidence level for a lower or upper nonparametric tolerance bound is given by:
1 - binomial distribution(1-p, n, k)
where
p = proportion
n = sample size
and
k is the order statistic defined by the lowest and upper rank specifications. For a lower tolerance bound, k is the 1 + lowest rank order statistic. For an upper tolerance bound, k is the n + highest rank order statistic.
The confidence level for a nonparametric tolerance interval is given by:
binomial distribution (p, n, k).
where
p = proportion
n = sample size
and
k is the (n + highest rank - lowest rank - 2) order statistic.