Power for One Sample Variance
Use the Power for One Sample Variance Explorer to determine a sample size for a hypothesis test about one variance. Select DOE > Sample Size Explorers > Power > Power for One Sample Variance. Explore the trade-offs between sample size, power, significance, and the hypothesized difference to detect (defined as a ratio between the null and alternative hypothesis values). Sample size and power are associated with the following hypothesis test:
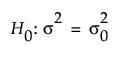
versus the two-sided alternative:
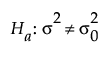
or versus a one-sided alternative:
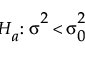 or
or 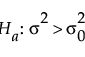
where σ2 is the true variance and σ20 is the null variance or reference value. The difference to detect is an amount away from σ0 that one considers as important to detect based on a set of samples. This difference is expressed as the ratio of your assumed variance under the alternative hypothesis to your null variance. For the same significance level and power, a larger sample size is needed to detect a small difference in variances than to detect a large difference. It is assumed that the population of interest is normally distributed with mean μ and standard deviation σ2.
Power Explorer for One Sample Variance Settings
Set study assumptions and explore sample sizes by using the radio buttons, text boxes, and menus. The profiler updates as you make changes to the settings. Alternatively, you can change the settings by dragging the cross hairs on the profiler curves.
Test Type
Specifies a one- or two-sided hypothesis test.
Alpha
Specifies the probability of a type I error, which is the probability of rejecting the null hypothesis when it is true. It is commonly referred to as the significance level of the test. The default alpha level is 0.05.
Power Explorer for One Sample Variance Profiler
The profiler enables you to visualize the impact of sample size assumptions on the power calculations. Interactive profiler changes to the sample size or Variance Ratio update the calculated power. Interactive changes to the profiler power update the sample size. To solve for a specific variable, use the target variable setting and click Go.
Target Variable
Enables you to solve for sample size or the variance ratio at a specified power.
Power
Specifies the probability of rejecting the null hypothesis when it is false. With all other parameters fixed, power increases as sample size increases.
Sample Size
Specifies the total number of observations (runs, experimental units, or samples) that are needed for your experiment.
Variance Ratio
Specifies the ratio of the variance under the null hypothesis (reference variance) to the variance under the alternative hypothesis (expected variance).
Power Explorer for One Sample Variance Options
The Explorer red triangle menu and report buttons provide additional options:
Simulate Data
Opens a data table of simulated data that are based on the explorer settings. View the simulated response column formula for the settings that are used. Run the table script to analyze the simulated data.
Make Data Collection Table
Creates a new data table that you can use for data collection. The table includes scripts to facilitate data analysis.
Remember Settings
Saves the current settings to the Remembered Settings table. This enables you to save a set of alternative study plans. See Remembered Settings in the Sample Size Explorers.
Reset to Defaults
Resets all parameters and graphs to their default settings.
The Profiler red triangle menu contains the following option:
Optimization and Desirability
Enables you to optimize settings. See “Desirability Profiling and Optimization” in Profilers.
Note: The sample size explorer report can be saved as a *.jmpdoe file. Open the file to return to the explorer. An alert prompts you to save the file.
Statistical Details for the Power Explorer for One Sample Variance
The power calculations for testing the variance of one sample group is based on the χ2 test. Calculations are based on the form of the alternative hypothesis.
For a one-sided, higher alternative (σ2 > σ20):
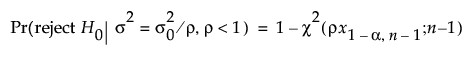
for a one-sided, lower alternative (σ < σ0):
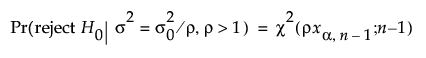
for a two-sided alternative (σ ≠ σ0):
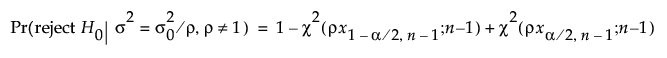
where:
α is the significance level
n is the sample size
ρ = σ2a / σ02
x1-α,n is the (1 - α)th quantile of a central χ2 distribution with ν degrees of freedom
χ2(x, ν) is the cumulative distribution function of a central χ2 distribution with ν degrees of freedom.