Stability Analysis
Stability Analysis
In the Mixed Model personality of the Fit Model platform, the Stability Analysis option is available when there is a fixed time variable, a random blocking variable, and their interaction effect is included as a random effect. The time variable must be continuous. The Stability Analysis option provides several techniques for shelf life estimation that use mixed model methodology. Shelf life refers to a set amount of time during which a product, usually a drug, is still safe and effective to use. This amount of time is determined by finding the point at which some measurable characteristic crosses a specified acceptance criterion. You can estimate the shelf life of a product by analyzing a test set of batches and determining when each batch crosses the acceptance criterion. The shelf life is then based on the mean distribution of the batches. Mixed model techniques can improve shelf life estimates as compared to traditional, fixed effects models.
Tip: You can perform a stability analysis that has multiple acceptance criteria by specifying multiple responses and using the broadcast feature when selecting the Stability Analysis option. The options that are specified in the Shelf Life Prediction window are then used for each response. If you want to do an analysis with multiple responses, it is best to use the specification limits column property to specify the limits.
When you select the Stability Analysis option, the Shelf Life Prediction window that appears enables you to specify the prediction method, quantile, confidence level, a one-sided or two-sided interval, and specification limits.
Prediction Method
Specifies the prediction method for predicting the shelf life. Each method uses the linear mixed model that treats the batch as a random blocking variable. The following prediction methods are available:
Quantile Line
Uses the linear mixed model to determine an interval such that 1 - quantile of the batches are within the acceptance criterion. The estimated shelf life is based on the lower or upper limit of that interval.
Confidence Interval on Quantile
Uses the linear mixed model to determine an interval such that 1 - quantile of the batches are within the acceptance criterion. Then, a 1 - α confidence bound is created around the estimated quantile interval. The estimated shelf life is based on the lower or upper limit of the confidence interval of the quantile.
Tolerance Interval
Uses the linear mixed model to determine a tolerance interval such that 1 - quantile of the batches are within the acceptance region. The estimated shelf life is based on the lower or upper limit of that tolerance interval. See Schwenke et al. (2020).
Quantile
Specifies the quantile that determines the shelf life estimate. This ensures that 1 - quantile of the batches do not cross the acceptance criterion within the estimated shelf life.
Confidence Levels
Specifies the α level for the confidence interval on quantile and tolerance interval methods.
One-Sided/Two-Sided
Specifies a one-sided or two-sided interval. If both lower and upper specification limits are defined, the default is a two-sided interval.
Limit
Specifies the specification limits. The limits define the acceptance criterion. If a specification limit is defined in a column property, the values from the column property are used by default.
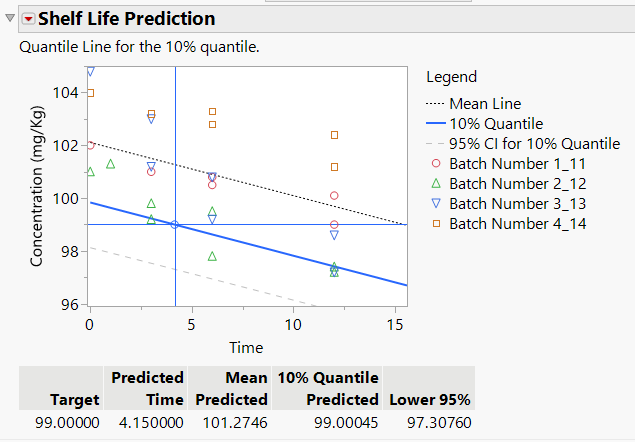
When you click OK, a Shelf Life Prediction report is added to the report window. The report contains a plot and a table.
Figure 8.12 Shelf Life Prediction Report
The plot shows the individual observations for the batches as well as lines for the mean, quantile, and specified intervals. The table contains information that is based on the options that were specified in the Shelf Life Prediction window.
Target
The specified acceptance criterion value.
Predicted
The value of the time variable at the intersection of the specification limit and the line for the specified prediction method. This is the value that is used to estimate the shelf life.
Mean Predicted
The marginal mean prediction at the predicted time.
The remaining columns in the table depend on the prediction method and whether a one-sided or two-sided interval is specified.