Statistical Details for Discrete Distributions
This section contains statistical details for the options in the Discrete Fit menu in the Distribution platform. Unless otherwise specified, confidence intervals for parameter estimates use likelihood-based calculations. For more information about likelihood-based confidence intervals, see “Statistical Details for Profile Likelihood Confidence Limits” in Predictive and Specialized Modeling. If the Y column has a Detection Limits column property, the Continuous Fit options fit a censored distribution and only a subset of distributions are available. For more information about fitting distributions to censored data, see Meeker and Escobar (1998).
Poisson
The Poisson distribution is defined by a single scale parameter λ > 0.
pmf: 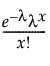 for 0 ≤ λ < ∞; x = 0,1,2,...
for 0 ≤ λ < ∞; x = 0,1,2,...
E(x) = λ
Var(x) = λ
Since the Poisson distribution is a discrete distribution, the overlaid fitted distribution is a step function, with steps that occur at each integer value.
Negative Binomial
The negative binomial distribution is defined by two parameters; mean λ and dispersion σ. The negative binomial distribution is useful for modeling the number of successes before a specified number of failures.
pmf: 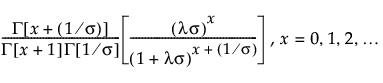
E(x) = λ
Var(x) = λ + σλ2
where Γ(·) is the Gamma function.
Relationship between Negative Binomial and Gamma Poisson Distributions
The negative binomial distribution is equivalent to the Gamma Poisson distribution. The Gamma Poisson distribution is useful when the data are a combination of several Poisson(μ) distributions and each Poisson(μ) distribution has a different μ.
The Gamma Poisson distribution results from assuming that x|μ follows a Poisson distribution and μ follows a Gamma(α,τ). The Gamma Poisson has parameters λ = ατ and σ = τ+1. The parameter σ is a dispersion parameter. If σ > 1, there is over dispersion, meaning there is more variation in x than explained by the Poisson alone. If σ = 1, x reduces to Poisson(λ).
pmf: 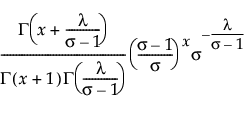 for 0 < λ; 1 ≤ σ; x = 0,1,2,...
for 0 < λ; 1 ≤ σ; x = 0,1,2,...
E(x) = λ
Var(x) = λσ
where Γ(·) is the Gamma function.
The Gamma Poisson is equivalent to a Negative Binomial with σnegbin = (σgp - 1) / λgp.
Run demoGammaPoisson.jsl in the JMP Samples/Scripts folder to compare a Gamma Poisson distribution with parameters λ and σ to a Poisson distribution with parameter λ.
ZI Poisson
The zero-inflated (ZI) Poisson distribution is defined by two parameters; scale λ > 0 and zero-inflation proportion π.
pmf: 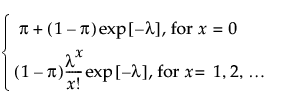
E(x) = (1 - π)λ
Var(x) = λ(1 - π)(1 + λπ)
ZI Negative Binomial
The zero-inflated (ZI) negative binomial distribution is defined by three parameters; λ > 0, dispersion σ > 0, and zero-inflation proportion π.
pmf: 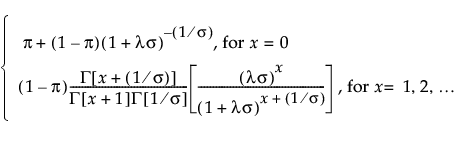
E(x) = (1 - π)λ
Var(x) = λ(1 - π)[1 + λ(σ + π)]
Binomial
The Binomial distribution is defined by two parameters; proportion of successes p and sample size n.
pmf: 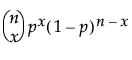 for 0 ≤ p ≤ 1; x = 0,1,2,...,n
for 0 ≤ p ≤ 1; x = 0,1,2,...,n
E(x) = np
Var(x) = np(1-p)
where n is the number of independent trials.
Note: The confidence interval for the binomial parameter is a profile likelihood interval.
Beta Binomial
The beta binomial distribution is useful when the data are a combination of several binomial distributions and each with a different p. One example is the overall number of defects from multiple manufacturing lines, each with a different mean number of defects (p).
The beta binomial distribution results from assuming that x|π follows a Binomial(n, π) distribution and π follows a Beta(α, β) distribution. The beta binomial is defined by two parameters; p = α/(α+β) and δ = 1/(α+β+1). The parameter δ is a dispersion parameter. When δ > 0, there is over dispersion, meaning there is more variation in x than explained by the binomial alone. When δ < 0, there is under dispersion. When δ = 0, x is distributed as binomial(n, p). The beta binomial exists only when n ≥ 2.
pmf: 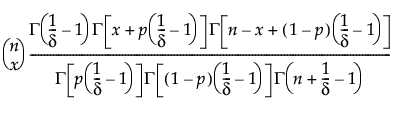
for 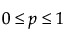 ;
; 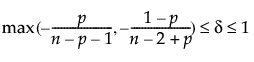 ; x = 0,1,2,...,n
; x = 0,1,2,...,n
E(x) = np
Var(x) = np(1-p)[1+(n-1)δ]
where Γ(·) is the Gamma function.
Remember that x|π ~ Binomial(n,π), while π ~ Beta(α,β). The parameters p = α/(α+β) and δ = 1/(α+β+1) are estimated by the platform. To obtain estimates of α and β, use the following formulas:
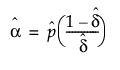
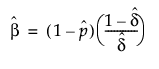
If the estimate of δ is 0, the formulas do not work. In that case, the beta binomial has reduced to the Binomial(n,p), and 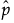 is the estimate of p.
is the estimate of p.
The confidence intervals for the beta binomial parameters are profile likelihood intervals.
Run demoBetaBinomial.jsl in the JMP Samples/Scripts folder to compare a beta binomial distribution with dispersion parameter δ to a Binomial distribution with parameters p and n = 20.
ZI Binomial
The ZI Binomial is defined by three parameters; the proportion of successes p, sample size n, and the zero-inflation proportion π.
pmf: 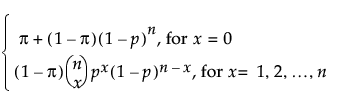
E(x) = (1-π)np
Var(x) = (1-π)[np(1-p) + n2p2] - [(1-π)np]2
where n is the number of independent trials.
ZI Beta Binomial
The ZI Beta Binomial is defined by four parameters; p = α/(α+β), δ = 1/(α+β+1), sample size n, and the zero-inflation proportion π. The ZI beta binomial exists only when n ≥ 2.
pmf: 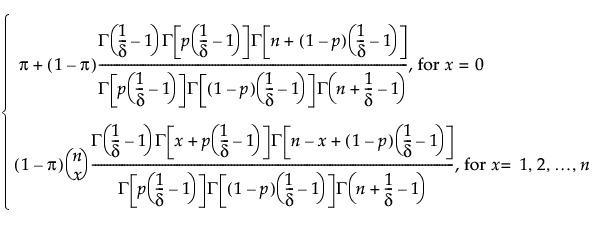
E(x) = (1-π)np
Var(x) = (1-π)np[(1-p)(1 + (n-1)δ) + np] - [(1-π)np]2
where n is the number of independent trials.