Validation Details
This section describes summary statistics when a validation method is used.
Validation and Test Set Statistic Definitions
This section defines RSquare Validation and RASE Validation. RSquare Test and RASE Test are computed for the test set in a completely analogous fashion.
Continuous Response
RSquare Validation
An R-square measure for the validation set that is computed as follows:
– For each observation in the validation set, compute the prediction error. The prediction error is the difference between the actual response and the response that is predicted by the training set model.
– Square and sum the prediction errors to obtain SSEValidation.
– Square and sum the differences between the actual responses in the validation set and their mean. This is the SSTValidation.
– RSquare Validation is:
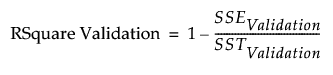
Note: It is possible for RSquare Validation to be negative.
RASE Validation
The square root of the mean squared prediction error for the validation set. This is computed as follows:
– For each observation in the validation set, compute the prediction error. The prediction error is the difference between the actual response and the response that is predicted by the training set model.
– Square and sum the prediction errors to obtain the SSEValidation.
– Denote the number of observations in the validation set by nValidation.
– RASE Validation is:
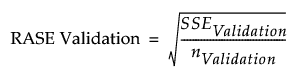
Binary Nominal or Ordinal Response
RSquare Validation
An Entropy R-square measure (also known as McFadden’s R2) for the validation set that is computed as follows:
– A model is fit by using the training set.
– Predicted probabilities are obtained for all observations.
– Using the predicted probabilities that are based on the training set model, the likelihood for the model is computed for observations in the validation set. Call this quantity Likelihood_FullValidation.
– Using the data in the validation set, the likelihood of the reduced model (no predictors) is computed. Call this quantity Likelihood_ReducedValidation.
– RSquare Validation is:
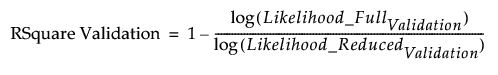
Note: It is possible for RSquare Validation to be negative.
Avg Log Error Validation
The average log error for the validation set is computed as follows:
– For each observation in the validation set, compute the log of its predicted probability as determined by the model that is based on the training set.
– Sum these logs, divide by the number of observations in the validation set, and take the negative of the resulting value.
Tip: Smaller values of Avg Log Error Validation are desirable.
RSquare K-Fold Statistic
If you conduct k-fold cross validation, the RSquare K-Fold statistic appears to the right of the other statistics in the Stepwise Regression Control panel. RSquare K-Fold is calculated as follows:
1 - Sum(SSE)/Sum(SST)
where:
SSE represents a vector of the error sum of squares in each of the k folds
SST represents a vector of the total sum of squares in each of the k folds
K-fold cross validation randomly divides the data into k subsets. In turn, each of the k sets is used as a validation set while the remaining data are used as a training set to fit the model. In total, k models are fit and k validation statistics are obtained. The model that produces the best validation statistic is chosen as the final model.