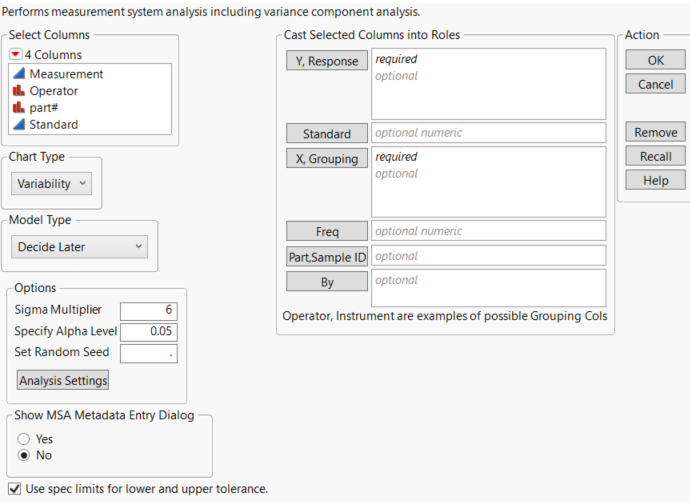
Launch the Variability Gauge Chart Platform
Launch the Variability Chart platform by selecting Analyze > Quality and Process > Variability/Attribute Gauge Chart. Set the Chart Type to Variability.
Figure 6.3 The Variability Chart Launch Window
For more information about the options in the Select Columns red triangle menu, see Column Filter Menu in Using JMP.
Chart Type
Choose between a variability gauge analysis (for a continuous response) or an attribute gauge analysis (for a categorical response, usually “pass” or “fail”).
Note: The content in this chapter covers only the Variability chart type. For more information about the Attribute chart type, see Attribute Gauge Charts.
Model Type
Choose the model type (Main Effect, Crossed, Nested, Crossed then Nested or Nested then Crossed). See Statistical Details for Variance Components.
Options
Contains the following options:
Sigma Multiplier
Specifies the sigma multiplier used in the analyses. The default value is 6.
Specify Alpha Level
Specifies the significance level used in the analyses.
Set Random Seed
Enables you to set a specific random seed.
Analysis Settings
Enables you to specify the method for computing variance components. See Analysis Settings.
Show MSA Metadata Entry Dialog
Specifies if the MSA Metadata dialog is shown after you click OK. This dialog enables you to load the metadata from a data table or enter the metatdata for each column manually. Use the following options to enter the metadata manually:
Choose Tolerance Entry Type
Choose to enter the tolerance range directly or specify the lower and upper tolerance values. If you choose to enter lower and upper tolerance values, the tolerance range is calculated as the difference between the upper and lower tolerance values. If only one tolerance value is entered, the tolerance range cannot be calculated and any statistics in the report that rely on the tolerance range are not shown.
Tolerance Range
Specifies the tolerance for the process, which is the difference between the upper specification limits and the lower specification limits.
Lower Tolerance
Specifies the lower tolerance limit. This is used to calculate the tolerance range if it is not specified directly.
Upper Tolerance
Specifies the upper tolerance limit. This is used to calculate the tolerance range if it is not specified directly.
Historical Mean
Specifies a historical mean. The historical mean is used to compute tolerance ranges for one-sided specification limits, either USL-Historical Mean or Historical Mean-LSL. If you do not enter a historical mean, the grand mean is used.
Historical Process Sigma
Specifies a historical process sigma. This value is used for calculations in the Gauge R&R Report and the Linearity Study.
Tip: This data can also be specified prior to launching by applying the MSA column property. You can apply the MSA column property to several measurement columns at once using Manage Limits. See Manage Limits.
Use spec limits for lower and upper tolerance
If a tolerance range is not specified for a column, but the column has a Spec Limits column property, this option uses the specification limits to calculate the tolerance range.
Y, Response
Specifies the measurement column. Specifying more than one Y column produces a separate variability chart for each response.
Standard
Specifies a standard or reference column that contains the “true” or known values for the measured part. Including this column enables the Bias and Linearity Study options. These options perform analysis on the differences between the observed measurement and the reference or standard value. See Bias Report and Linearity Study.
X, Grouping
Specify the classification columns that group the measurements. If the factors form a nested hierarchy, specify the higher terms first. If you are doing a gauge study, specify the operator first and then the part.
Freq
Identifies the data table column whose values assign a frequency to each row. Can be useful when you have summarized data.
Part, Sample ID
Identifies the part or sample that is being measured.
By
Identifies a column that creates a report consisting of separate analyses for each level of the variable.
Data Format
To use the Variability Chart platform, all response measurements must be in a single response column. Sometimes, responses are recorded in multiple columns, where each row is a level of a design factor and each column is a level of a different design factor. Data that are in this format must be stacked before running the Variability Chart platform. See Stack Columns in Data Tables in Using JMP.