Confidence Interval for Two Independent Sample Proportions
Use the Confidence Interval for Two Independent Sample Proportions Explorer to determine a sample size for a confidence interval for the difference in two proportions, for log relative risk, or for log odds. Select DOE > Sample Size Explorers > Confidence Intervals > Confidence Interval for Two Independent Sample Proportions. Explore the trade-offs between sample size, significance, assumed proportions, and the margin of error for your interval.
Interval Explorer Two Independent Sample Proportions Settings
Set study assumptions and explore sample sizes by using the radio buttons, text boxes, and menus. The profiler updates as you make changes to the settings. Alternatively, you can change the settings by dragging the cross hairs on the profiler curves.
Interval Type
Specifies the type of interval. Specify Bound for a one-sided interval. Specify Interval for a two-sided interval.
Alpha
Specifies the confidence level, 1 - Alpha. The default alpha level is 0.05 for a 95% confidence interval.
Interval Purpose
Difference in Proportions
Specifies a confidence interval for the difference in two proportions (p1 - p2).
Log Relative Risk
Specifies a confidence interval for the relative risk (p1/p2) on a log scale.
Log Odds Ratio
Specifies a confidence interval for the odds ratio (p1/(1-p1))/(p2/(1-p2)) on a log scale.
Interval Explorer Two Independent Sample Proportions Profiler
The profiler enables you to visualize the impact of sample size assumptions on the margin of error calculations. Interactive profiler changes to the sample sizes or standard deviations update the calculated power. Interactive changes to the profiler power update the sample sizes. To solve for a specific variable, use the target variable setting and click Go.
Target Variable
Enables you to solve for a sample size or a group proportion.
Margin of Error
Specifies the half-width of the interval or the width of a one-sided interval. With all other parameters fixed, margin of error decreases as sample size increases.
Ratio of Group 2 to Group 1 Sample Size
Specifies the ratio between group sample sizes. For equal group sample sizes, set to one.
Note: The ratio can shift as you explore changes to the assumptions due to the mathematical search routines.
Total Sample Size
Specifies the total number of observations (runs, experimental units, or samples) that are needed for your experiment.
Group 1 Sample Size
Specifies the number of observations (runs, experimental units, or samples) that are needed for Group 1 in your experiment.
Group 2 Sample Size
Specifies the number of observations (runs, experimental units, or samples) that are needed for Group 2 in your experiment.
Note: Adjusting the total sample size adjusts the sample size in each group according to the ratio of sample size setting. Adjusting the sample size for one group adjusts the sample size in the other group holding the total sample size fixed.
Group 1 Proportion
Specifies the assumed proportion for Group 1.
Group 2 Proportion
Specifies the assumed proportion for Group 2.
Interval Explorer Two Independent Sample Proportions Options
The Explorer red triangle menu and report buttons provide additional options:
Simulate Data
Opens a data table of simulated data that are based on the explorer settings. View the simulated response column formula for the settings that are used.
Make Data Collection Table
Creates a new data table that you can use for data collection. The table includes scripts to facilitate data analysis.
Save Settings
Saves the current settings to the Saved Settings table. This enables you to save a set of alternative study plans. See Remembered Settings in the Sample Size Explorers.
Reset to Defaults
Resets all parameters and graphs to their default settings.
Statistical Details for the Confidence Interval for Two Independent Sample Proportions Explorer
The calculations for each interval type are based on normal approximations.
Difference in Proportions
For intervals about the difference in proportions the margin of error (MOE) for a two-sided confidence interval is calculated as follows:
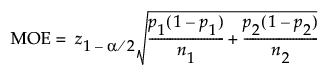
The MOE for a one-sided interval is calculated as follows:
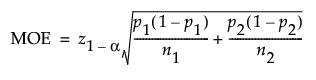
Log Relative Risk
For the logarithm of the relative risk the margin of error (MOE) is calculated as follows:
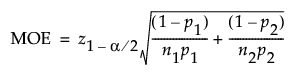
The MOE for a one-sided interval is calculated as follows:
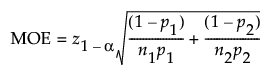
Log Odds Ratio
For the logarithm of the odds ratio, the margin of error is calculated as follows:
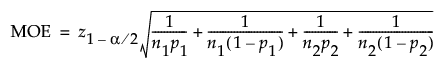
The MOE for a one-sided interval is calculated as follows:
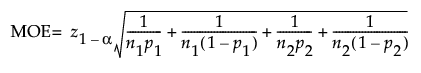
where:
α is the significance level
n1 and n2 are the group sample sizes
p1 and p2 are the group proportions
z1-α is the (1 - α)th quantile of the distribution.