Model Averaging
In the Stepwise personality of the Fit Model platform, the Model Averaging option combines multiple models into a single model. The resulting weighted average model can have better prediction capability than each of the single models. The Model Averaging option is useful for avoiding a model that overfits your data. When many terms are selected into a model, the fit tends to inflate the parameter estimates. Model averaging often shrinks the estimates on the weaker terms, which can yield better predictions. The models are averaged with respect to the AICc Weight of each model, which is calculated as follows:
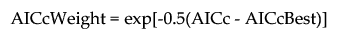
The AICc Best value is the smallest AICc value among the fitted models. The AICc Weight values are calculated for each model and scaled to sum to 1. The scaled AICc Weight values that are less than one minus the specified Cumulative AICc Weight Cutoff value are set to zero. This action eliminates the use of weak models in the averaged model. The parameters for the averaged model are the weighted averages of the parameter estimates across the models that have nonzero AICc Weight values. Similarly, the reported standard errors are also weighted. The AICc weights are used to calculate a weighted average of the squared standard errors for each estimate. The square root of that estimate is reported as the Std Error in the Model Averaging report.