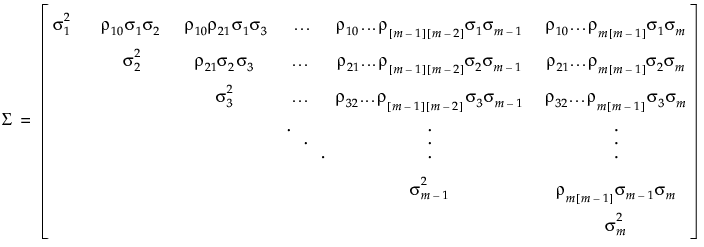|
•
|
|
•
|
Here tj is the time of observation j. In this structure, observations taken at any given time have the same variance, 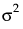 . The parameter ρ, where -1 < ρ < 1, is the correlation between two observations that are one unit of time apart. As the time difference between observations increases, their covariance decreases because ρ is raised to a higher power. In many applications, AR(1) provides an adequate model of the within subject correlation, providing more power without sacrificing Type I error control.
. The parameter ρ, where -1 < ρ < 1, is the correlation between two observations that are one unit of time apart. As the time difference between observations increases, their covariance decreases because ρ is raised to a higher power. In many applications, AR(1) provides an adequate model of the within subject correlation, providing more power without sacrificing Type I error control.
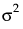 . The parameter ρ, where -1 < ρ < 1, is the correlation between two observations that are one unit of time apart. As the time difference between observations increases, their covariance decreases because ρ is raised to a higher power. In many applications, AR(1) provides an adequate model of the within subject correlation, providing more power without sacrificing Type I error control.
. The parameter ρ, where -1 < ρ < 1, is the correlation between two observations that are one unit of time apart. As the time difference between observations increases, their covariance decreases because ρ is raised to a higher power. In many applications, AR(1) provides an adequate model of the within subject correlation, providing more power without sacrificing Type I error control.In the Toeplitz structure, observations that are separated by a fixed number of time units have the same correlation. In contrast to the AR(1) correlation structure, the Toeplitz correlations at a fixed time difference are arbitrary. Denote the correlation for observations d units apart by 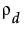 . The correlation matrix is as follows:
. The correlation matrix is as follows:
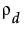 . The correlation matrix is as follows:
. The correlation matrix is as follows:The antedependence model is a general model that is flexible and allows the correlation structure to change over time. In this model, the correlation between two observations at adjacent time points j - 1 and j is unique and is denoted 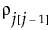 .
.
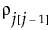 .
.The correlation between pairs of observations at non-adjacent time points j and j’ is the product of all the adjacent correlations in between. This is written as follows:
For example, the correlation between the pair of observations at time points j=2 and j’=6 would be 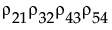 .
.
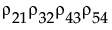 .
.|
•
|
The Antedependent structure allows the variance among observations at any given time to vary. Denote the variance among observations taken at time j is
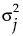 . Then the covariance matrix is as follows: . Then the covariance matrix is as follows: |
 Repeated Covariance Structures
Repeated Covariance Structures Unequal Variances Covariance Structure
Unequal Variances Covariance Structure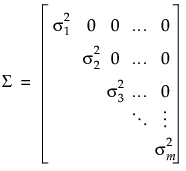
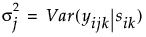
 Unstructured Covariance Structure
Unstructured Covariance Structure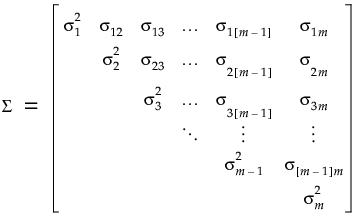
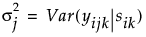
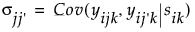
 Compound Symmetry Covariance Structure
Compound Symmetry Covariance Structure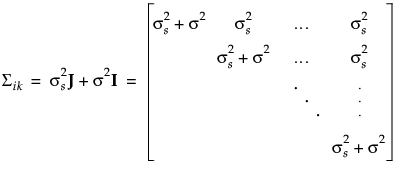
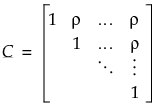
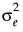 , among observations taken at any time point. The covariance structure is then
, among observations taken at any time point. The covariance structure is then 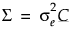 where
where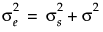
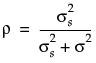 .
.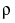 is the intra-class correlation coefficient and
is the intra-class correlation coefficient and 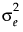 is the residual variance. Another option is to use the Compound Symmetry Unequal Variances structure in JMP, which allows the variance to vary across time points. This leads to a covariance matrix as follows:
is the residual variance. Another option is to use the Compound Symmetry Unequal Variances structure in JMP, which allows the variance to vary across time points. This leads to a covariance matrix as follows: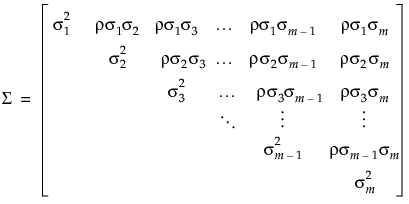
 AR(1) Covariance Structure
AR(1) Covariance Structure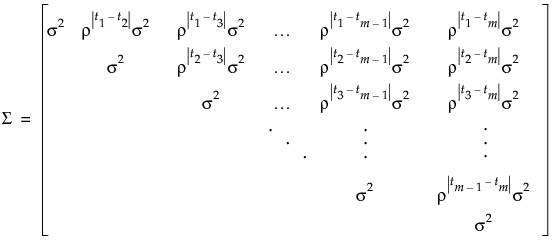
 Toeplitz Covariance Structure
Toeplitz Covariance Structure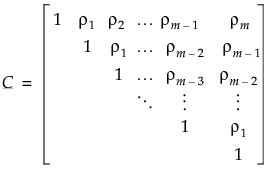
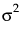 , for observations from any time point. The covariance structure is
, for observations from any time point. The covariance structure is 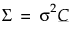 .
.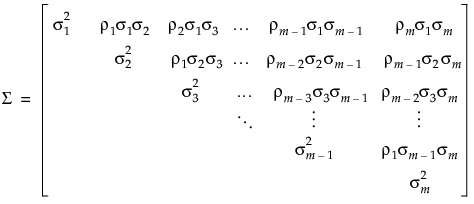


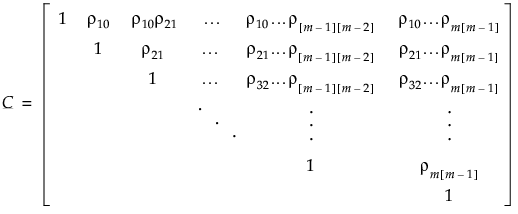
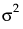 and the covariance matrix is
and the covariance matrix is 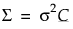 .
.