 Analysis of Causal Effects
Analysis of Causal Effects
The contents of the Analysis of Causal Effects section in the Causal Treatment model report depends on the treatment type.
 Binary Treatment
Binary Treatment
When the treatment is binary, the Analysis of Causal Effects section contains a table and an Average Treatment Effect for the Treated section. The Analysis of Causal Effects table shows information about the following estimates:
Potential Outcome Mean at Intervention Level 0
The expected value of the outcome if no observations received treatment.
Potential Outcome Mean at Intervention Level 1
The expected value of the outcome if every observation received treatment.
ATE
The average treatment effect. This is the difference between the two potential outcome means.
For each parameter, the Analysis of Causal Effects table provides the estimate of the parameter (Estimate), the standard error of the estimate (Std Error), the lower 95% confidence interval bound (Lower 95%), the upper 95% confidence interval bound (Upper 95%), the Z-statistic (Z) and the p-value (Prob>|Z|). A short interpretation of the parameter estimates appears below the table when the Show Tips and Interpretations option is selected.
The Analysis of Causal Effects section also contains an Average Treatment Effect for the Treated (ATET) table. This table includes the same rows and columns as the Analysis of Causal Effects table, with the last row exchanging the ATE for the ATET. The ATET is calculated using only the observations in the sample that received treatment. Therefore, the values in this table might differ from the preceding table. The text prompted by the Show Tips and Interpretations option provides a reminder below this table that the ATET has a different interpretation than the ATE. Consider ATET results if you are interested only in the subpopulation that receives treatment. See Statistical Details for Causal Estimands and Estimators.
 Continuous Treatment
Continuous Treatment
When the treatment is continuous, the Analysis of Causal Effects section contains two subsections: A Marginal Structural Model (MSM) Results section and a Generalized Propensity Score (GPS) Model Results section.
Marginal Structural Model Results
The MSM results section table shows information about the fitted MSM with inverse probability weighting with ratio adjustment (IPWR). The table corresponds to the results table of a linear regression model with treatment and its square as predictors. This table shows information about the estimate, standard error, 95% confidence interval bounds, Z-statistic, and p-value for each coefficient in the model. The intercept estimate can be interpreted as the expected value of the outcome when the treatment level is 0. You can estimate a causal treatment effect between two levels using the MSM results by plugging treatment values x1 and x2 into the following equation:
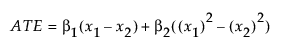
where β1 is the treatment coefficient estimate and β2 is the coefficient estimate for the square of the treatment.The square term is calculated after centering.
Generalized Propensity Score Model Results
The GPS model section contains a Predicted Potential Outcome Densities Grouped by Treatment Levels plot and an Estimated Potential Outcome Mean at each Treatment Level table.
The Predicted Potential Outcome Densities Grouped by Treatment Levels ridge plot displays predicted potential outcome densities at each specified treatment level. The treatment levels on the vertical axis correspond to the Treatment Level Minimum, Treatment Level Maximum, and Treatment Level Increment values in the Model Information section. Causal effects cannot be directly estimated from this plot. An interpretation of this plot is provided below the horizontal axis when the Show Tips and Interpretations option is selected in the Fit Causal Treatment red triangle menu.
In the Estimated Potential Outcome Mean at Each Treatment Level table, each row corresponds to the treatment levels specified in the Model Information section. For each treatment level, the average potential outcome estimate (Potential Outcome Mean at Level t), standard error (Std Error), and 95% confidence interval bounds (Lower 95% and Upper 95%) are reported. To estimate a causal effect from this table corresponding to the GPS model, choose two treatment levels and take the difference between their potential outcome mean estimates.